Vela
The Vela project was started around 1959 as an ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) program to monitor nuclear test explosions around the globe. Vela consisted of three sub-projects:
- Vela Uniform: Detect sub-surface nuclear tests via seismic waves
- Vela Hotel: Detect nuclear explosions at long range in space with satellites
- Vela Sierra: Advanced satellites to also detect atmospheric nuclear tests
For Veta Hotel, TRW Inc. received a contract to build up to 10 satellites. Their design was of polyhedral shape, with a diameter of 1.37 m (54 in) and a height of 1.17 m (46 in). They were equipped with 12 external X-ray detectors and 18 internal neutron and gamma ray detectors. The surface was covered with solar cells to generate the power for the instruments. The Vela Hotel satellites were launched in pairs atop Atlas-Agena launchers, and were placed 180 degrees apart into very high circular orbits. Orbital radius was more than 100000 km, to avoid the particle radiation in the Van Allen belts. The first of three satellite pairs was launched on 17 October 1963, only a few days after the Partial Test Ban Treaty (which forbids nuclear tests under water, in the atmosphere and in space) came into effect. The satellites' design lifetime was only 6 months, but they actually remained operational for 5 years before being shut down. Because of this extended lifetime, two additional Vela Hotel launches were cancelled. The Vela Hotel program initially had the numerical designation Program 823, which was changed in 1964 to Program 638.
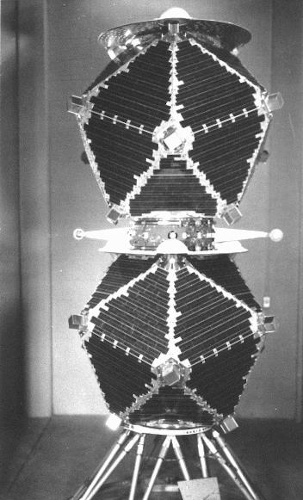 |
| Photo: USAF |
| Vela Hotel satellite pair |
Vela Hotel was succeeded by the Advanced Vela satellites, also built by TRW. They were heavier than the original series, launched by Titan IIIC boosters, and instrumented to also detect atmospheric nuclear explosions. For this, they used so-called "bhangmeters", measuring photon flux with a sub-millisecond resolution in time. Six Advanced Vela satellites were launched between April 1967 and April 1970. They were built with a design lifetime of 18 months, but lasted significantly longer - Vela 5A (Vela 9) was operational for 15 years. To succeed Vela, the nuclear detection mission was taken over as a secondary mission by other spacecraft, first the DSP and later the GPS satellites.
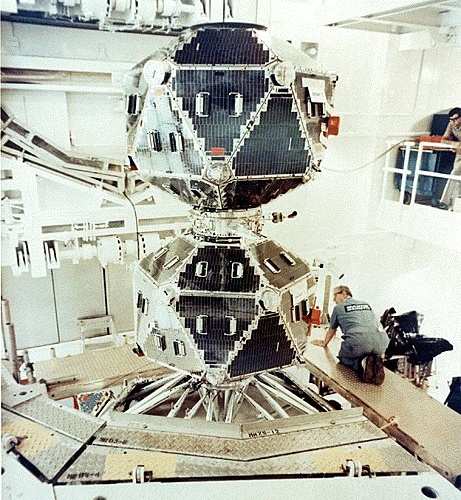 |
| Photo: Los Alamos National Laboratory, |
| Advanced Vela satellite pair (Vela 5A/5B) |
While the Vela satellites never detected an illegal nuclear endo- or exo-atmospheric test, their instruments were the first to detect the previously unknown Gamma Ray Bursts, extremely energetic events in distant galaxies.
Vela Launch List
- No.: Sequential flight number for the Vela program
- Name: The OPS number ("OPS" standing for "Operations") is a random number given to all military-related satellite launches between 1963 and May 1984 (when "OPS" was replaced by a sequential "USA" number).
- COSPAR ID: International designation of the satellite
| No. | Type | Name | COSPAR ID | Launch | Launch Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vela Hotel | Vela 1 (Vela 1A) Vela 2 (Vela 1B) | 1963-039A 1963-039C | 17 Oct 1963 | LV-3A Atlas-Agena D |
| 2 | Vela Hotel | Vela 3 (Vela 2A) / OPS 3662 Vela 4 (Vela 2B) / OPS 3674 | 1964-040A 1964-040B | 17 Jul 1964 | LV-3A Atlas-Agena D |
| 3 | Vela Hotel | Vela 5 (Vela 3A) / OPS 6577 Vela 6 (Vela 3B) / OPS 6564 | 1965-058A 1965-058B | 20 Jul 1965 | LV-3A Atlas-Agena D |
| 4 | Advanced Vela | Vela 7 (Vela 4A) / OPS 6638 Vela 8 (Vela 4B) / OPS 6679 | 1967-040A 1967-040B | 28 Apr 1967 | SLV-5C Titan IIIC |
| 5 | Advanced Vela | Vela 9 (Vela 5A) / OPS 6909 Vela 10 (Vela 5B) / OPS 6911 | 1969-046D 1969-046E | 23 May 1969 | SLV-5C Titan IIIC |
| 6 | Advanced Vela | Vela 11 (Vela 6A) / OPS 7033 Vela 12 (Vela 6B) / OPS 7044 | 1970-027A 1970-027B | 8 Apr 1970 | SLV-5C Titan IIIC |
Vela launches
Main Sources
[1] Wikipedia: Vela (Satellite)
[2] Gunter's Space Page (for launch lists)
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 3
Last Updated: 4 August 2025