Miscellaneous Castor-Based Rockets
(Castor / Castor 2R / Castor-Lance / Castor-Star 26C /
Talos-Castor)
The Thiokol Castor solid-fueled rocket motor was a derivative of Thiokol's Sergeant motor. It was widely used in large sounding rockets and launch vehicles of the 1950s to 1980s era. This article summarizes sounding rockets with a Castor stage, which were used in small numbers by the U.S. Air Force, but which are not mentioned in other articles of the Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles.
Castor / Castor 2R
In January 1967 (scramjet experiment) and April 1975 (plasma research), the USAF launched two unboosted Castor rockets. All other single-stage Castor launches used the Castor 2R variant with two small Recruit boosters attached to the first stage. The USAF launched a total of five Castor 2R rockets between January 1975 and December 1978. The last mission of these was labeled "DOT 1", and tested missile interceptor technology (see also Castor-Star 26C below).
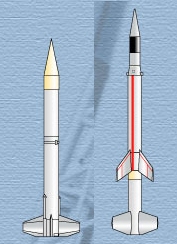 |
| Images: Orbital Sciences |
| Left: Castor 2R Right: Talos-Castor |
Castor-Lance
On 25 May 1973, the AFCRL (Air Force Cambridge Research Lab) launched a Castor-Lance rocket on an infrared aeronomy research mission, which reached an altitude of 569 km (354 miles). The second and final Castor-Lance was fired by the USAF on 17 June 1985 for the "BEAM" infrared astronomy experiment, but this mission is listed as a failure.
Castor-Star 26C (DOT)
Between February 1980 and June 1981, the U.S. Air Force launched three two-stage solid-fueled rockets consisting of two Recruit boosters, a Castor first stage and a Star 26C second stage. The test missions were named "DOT 2" to "DOT 4". The DOT missions are associated with missile interceptor technology tests, and there were indeed launches of LGM-30G Minuteman III ICBM on each of the DOT launch days.
Space Data Talos-Castor
Space Data Corporation made sounding rockets consisting of the booster of an RIM-8 Talos missile and a Castor stage. Of the eight launches of Talos-Castor rockets, six were by the USAF between November 1976 and April 1986. The payloads included plasma, aeronomy and auroral experiments.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for Castor 2R, Castor-Lance, Castor-Star 26C, Talos-Castor:
| Castor 2R | Castor-Lance | |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 8 m (26 ft) | ? |
| Diameter | 79 cm (31 in) | 1st stage: 79 cm (31 in) 2nd stage: 38 cm (15 in) |
| Weight | 5200 kg (11500 lb) | ? |
| Altitude | > 200 km (125 miles) | > 500 km (310 miles) |
| Propulsion * | Booster: 2x Thiokol XM19 Recruit; 156 kN (35000 lb) each for 1.5 s 1st stage: Thiokol Castor; 235 kN (52800 lb) for 38 s |
1st stage: Thiokol Castor; 235 kN (52800 lb) for 38 s 2nd stage: Thiokol TX-77 Lance; 227 kN (51000 lb) for 8.7 s |
| Castor-Star 26C | Talos-Castor | |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 11.6 m (38 ft) | 16.9 m (55.4 ft) |
| Diameter | 1st stage: 79 cm (31 in) 2nd stage: 66 cm (26 in) |
1st stage: 76 cm (30 in) 2nd stage: 79 cm (31 in) |
| Weight | 5500 kg (12100 lb) | 8200 kg (18100 lb) |
| Altitude | > 300 km (185 miles) | |
| Propulsion * | Booster: 2x Thiokol XM19 Recruit; 156 kN (35000 lb) each for 1.5 s 1st stage: Thiokol Castor; 235 kN (52800 lb) for 38 s 2nd stage: Thiokol Star 26C; 35 kN (7900 lb) for 16.8 s |
1st stage: ABL MK 11 MOD 2; 516 kN (116000 lb) for 5.2 s 2nd stage: Thiokol Castor; 235 kN (52800 lb) for 38 s |
Main Sources
[1] Jonathan McDowell: Launch Vehicles Database
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 4
Last Updated: 18 January 2006