Boeing SSB-7 IUS
To place geostationary satellites into orbit a multi-stage launch vehicle is required which, first, places the satellite into a low-Earth orbit, from where a separate stage flies the satellite into the geostationary orbit.
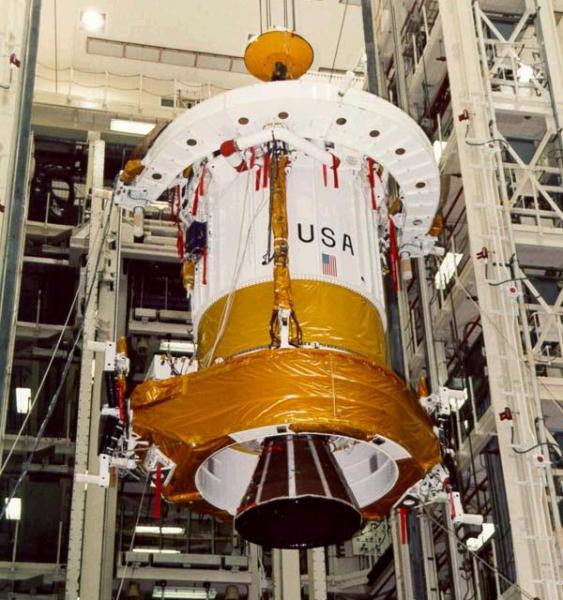 |
| Photo: Boeing |
| IUS (SSB-7A) |
The Boeing Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), which carried the military designation SSB-7A (probably only for the military flights), was developed to fulfill this function with the Space Shuttle, Titan 34D and Titan IV launch vehicles.
| Stage | Length | Diameter | Engine | Fuel | Thrust |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.50 m | 2.30 m | 1 United Tech. Orbus-21 | solid | 173,500 N |
| 2 | 3.50 m | 2.30 m | 1 United Tech. Orbus 6E | solid | 74,730 N |
Specifications for IUS
It was a two stage vehicle which is capable to transfer a payload of 2750 kg from low-Earth orbit to geostationary orbit.
| Stage | Length | Diameter | Engine | Fuel | Thrust |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.10 m | 1.60 m | 1 United Tech. Orbus 6 | solid | 78,416 N |
Specifications for IUS-2
A single stage version, known as IUS-2 was also used with the Titan 34D launch vehicle.
The IUS was used for the first time on 30 October 1982, and the 24th and last flight was on a Titan 402B on 14 February 2004. Of the 24 flights, one failed.
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 3
Last Updated: 16 March 2003