BG Series
(BG-1 through BG-3)
The BG designation was introduced by the U.S. Army Air Force in 1942, and covered unmanned gliders loaded with bombs or an explosive warhead. The BG gliders were similar in concept to the Navy's Glomb.
Fletcher BG-1
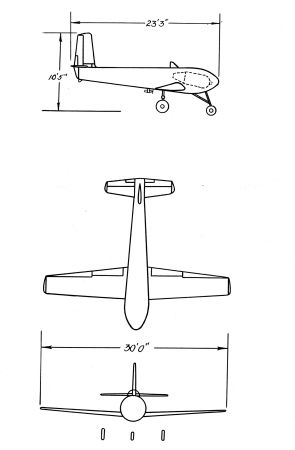
After the USAAF had cancelled the order for the Fletcher PQ-11A radio-controlled target drone, ten of the PQ-11As under construction were completed as XBG-1 bomb gliders. In the XBG-1, the PQ-11A's engine was replaced by a 900 kg (2000 lb) bomb. The XBG-1 was to be towed to the target area by a larger aircraft and upon release was to be guided to target impact by radio-commands using imagery transmitted from a TV camera in the glider's nose. No information on the XBG-1 test program is available, but the model was never used operationally.
Fletcher BG-2
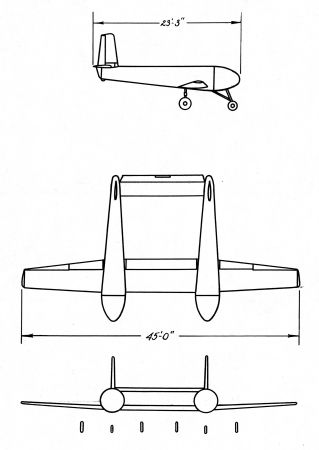
There is conflicting information about the Fletcher BG-2 design. Several sources, e.g. [2], report that when the Frankfort 8-seat XCG-1 troop-carrying glider was cancelled in 1941, the three XCG-1s under construction were completed by Fletcher as XBG-2 bomb gliders. Source [3] gives similar, but not identical, information, indicating that the XBG-2 was similar to the Frankfort XCG-2, a scaled-up 15-seat derivative of the XCG-1. However, the XBG-2 drawing below shows a design which is essentially two XBG-1 fuselages joined by common center wing and tail sections. This design is reported to have carried two 900 kg (2000 lb) bombs. Since no source can be dismissed as erroneous at the momemt, it is not clear which configuration of the XBG-2 was actually built. Most likely one of the designs (converted cargo glider or twin XBG-1) was discarded in favour of the other. In any case, no information about the results of tests (if any!) is available, and the BG-2 program was cancelled in 1942.
 |
 | |
| Drawings: via George Cully | ||
| XBG-1 | XBG-2(?) | |
Source [4] presents yet another completely different story! It says, that the XBG-2 was a derivative of Fletcher's CQ-1A drone control aircraft, and even provides a photograph. If the aircraft on the photo is actually an XBG-2 (which is far from certain!), then the model was indeed derived from the CQ-1, and the other account, that the XBG-2 was derived from the CG-1, might have its origins by a Q→G typo.
 |
| Photo: National Museum of the USAF |
| XBG-2(?) |
All said, in the moment there is no reliable information about the nature of the XBG-2 design available.
Cornelius BG-3
The BG-3 was a design with nose-mounted horizontal stabilizers and forward-swept wings. As such it was similar to Cornelius' XFG-1 fuel glider. Although the USAAF had planned to procure one XBG-3 prototype, this order was cancelled in 1942.
Specifications
Except for the dimensions in the drawings, no information on the specifications of the BG designs is available.
Main Sources
[1] Bill Gunston: "The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Rockets and Missiles", Salamander Books Ltd, 1979
[2] John M. Andrade: "U.S. Military Aircraft Designations and Serials, 1909 to 1979", Midland Counties, 1979
[3] US Army Air Forces: "Army Aircraft Model Designations", 1945 & 1946 editions
[4] Bill Norton: "American Military Glider Experiments of WWII", AAHS Journal Vol. 53 No. 2, Summer 2008
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 1
Last Updated: 25 June 2009